Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Editorial
- Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Jin Wook Chung
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(2):235-237. Published online July 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.06.29
- 877 Views
- 46 Downloads

Original Article
- Use of doxorubicin-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: a prospective study
- Su Jong Yu, Yun Bin Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hyo-Cheol Kim, Jin Wook Chung, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Yoon Jun Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):166-176. Published online March 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2023.02.08
- 2,075 Views
- 95 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
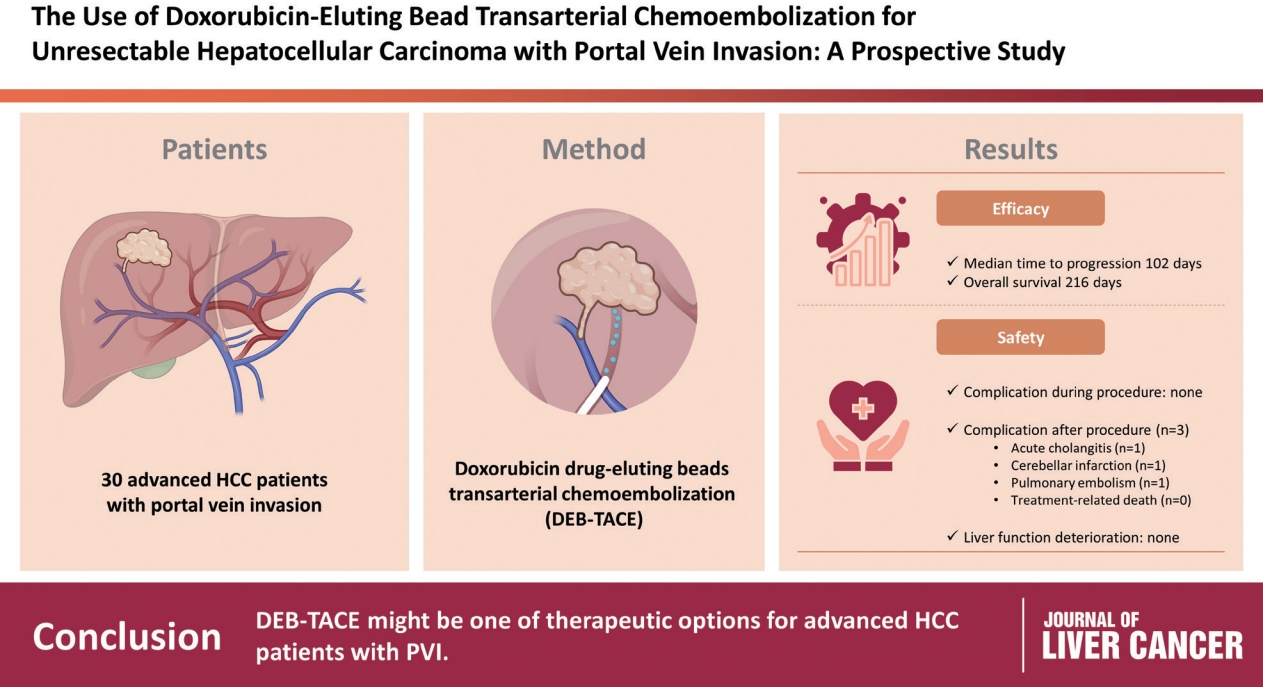
To evaluate the applicability of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment with doxorubicin drug-eluting beads (DEBs) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with portal vein invasion (PVI).
Methods
This prospective study was approved by the institutional review board and informed consent was obtained from all participants. A total of 30 HCC patients with PVI received DEB-TACE between 2015 and 2018. The following parameters were evaluated: complications during DEB-TACE, abdominal pain, fever, and laboratory outcomes, including liver function change. Overall survival (OS), time to progression (TTP), and adverse events were also analyzed and assessed.
Results
DEBs measuring 100–300 μm in diameter were loaded with doxorubicin (150 mg per procedure). There were no complications during DEB-TACE and no significant differences in the levels of prothrombin time, serum albumin, or total bilirubin at follow-up compared to baseline. The median TTP was 102 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 42–207 days) and the median OS was 216 days (95% CI, 160–336 days). Three patients (10%) had severe adverse reactions, including transient acute cholangitis (n=1), cerebellar infarction (n=1), and pulmonary embolism (n=1), but no treatment-related death occurred.
Conclusions
DEB-TACE may be a therapeutic option for advanced HCC patients with PVI.

Review Article
- Conventional Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Role of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Guidance
- In Joon Lee, Jin Wook Chung
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(1):19-29. Published online March 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.1.19

- 5,231 Views
- 145 Downloads
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Conventional chemoembolization using Lipiodol-based regimens was introduced in the 1980s, and it is currently recommended as the primary treatment modality for patients with unresectable, intermediate, or locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by the international guidelines. For better therapeutic efficacy and safety, chemoembolization should be performed as selectively as possible through tumor-feeding arteries, based on the detection of arterial supply to the HCC. With the technical advancement of flat-panel detector, cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is mounted on the C-arm of the angiographic machine. CBCT facilitates the detection of small occult HCCs and fine tumor-feeding arteries, recognition of extrahepatic collateral supply, navigation of a microcatheter to the target feeding arteries, prevention of non-target embolization, and intraprocedural assessment of the completeness of treatment with chemoembolization. These functions performed by CBCT ultimately improve the safety and efficacy of chemoembolization and may contribute to improving the prognosis of the patient with HCC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2023 Expert Consensus-Based Practical Recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Korean Journal of Radiology.2023; 24(7): 606. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 241. CrossRef - Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2023 Expert consensus-based practical recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Yuri Cho, Jin Woo Choi, Hoon Kwon, Kun Yung Kim, Byung Chan Lee, Hee Ho Chu, Dong Hyeon Lee, Han Ah Lee, Gyoung Min Kim, Jung Suk Oh, Dongho Hyun, In Joon Lee, Hyunchul Rhim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 521. CrossRef - The efficacy of TACE; how can automated feeder software help?
Hassan Abdelsalam, Doaa M. Emara, Ehab M. Hassouna
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2023 Expert Consensus-Based Practical Recommendations of the Korean Liver Cancer Association

Original Article
- Transarterial Chemoembolization versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Small Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Discrepant Features on Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Young Youn Cho, Jung Hee Kwon, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Jeong Min Lee, Jae Young Lee, Hyo-Choel Kim, Jin Wook Chung, Won-mook Choi, Eun Ju Cho, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Chung Yong Kim, Hyo-Suk Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(1):19-29. Published online March 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.1.19
- 1,210 Views
- 8 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: This study compared the outcomes of patients with small hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) who were treated using transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) or radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Methods
This was a post-hoc analysis of a prospective study that evaluated the diagnostic efficacy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). We analyzed 41 small hepatic nodules in 32 patients that showed typical radiologic hallmarks on both CT and gadoxate-enhanced MRI (typical nodules) and 25 small hepatic nodules from 22 patients that showed atypical radiologic hallmarks on CT and typical radiologic hallmarks on MRI (discrepant nodules).
Results
There were no significant differences in the baseline characteristics of the patients with typical and discrepant nodules. Complete response rates 1 month after TACE or RFA were 75.0% (18/24) and 94.1% (16/17; P=0.20), respectively, for the patients with typical nodules and 58.8% (10/17) and 100% (8/8; P=0.05), respectively, for the patients with discrepant nodules. Treatment failure rates after TACE or RFA were 33.3% (8/24) and 5.8% (1/17; P=0.15), respectively, for the patients with typical nodules and 47.0% (8/17) and 0.0% (0/8; P=0.02), respectively, for the patients with discrepant nodules. Among patients achieving complete response, there were no significant differences in the risk of marginal recurrence.
Conclusions
RFA provided higher complete response rates and significantly lower treatment failure rates than TACE for patients with discrepant nodules of HCC. Therefore, a treatment modality such as RFA may be preferable for small HCCs which show discrepancy on two imaging modalities.

Review Article
- Standardization of Conventional Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Jin Wook Chung
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):10-13. Published online February 28, 2012
- 467 Views
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In conventional chemoembolization for hepatocellula carcinoma, there are diversities in selecting chemotherapeutic drugs and
embolic materials and their delivery techniques. And there is no convincing evidence which one is better than the others. As a
result
, lack of standarized protocol has been indicated as a limitation of conventional chemoembolization. However, we have to understand that hepatic functional reserve and tumoral factors are more important prognostic factors than technical factors in chemoembolization. In patients with diverse hepatic function and tumoral status, it is practically impossible to apply standardized protocol of chemoembolization. Standardized protocol in chemoembolization may increase the risk of the procedure or decrease the therapeutic efficacy and, as a result, shorten the survival of the patients. Chemoembolization technique should be customized individually depending on hepatic functional reserve and tumoral factors. More importantly, we should keep the basic principle of chemoembolization. The most important basic principle is to perform superselective chemoembolization of all tumor feeders. Cone-beam CT and low-profile microcatheters may greatly help interventional radiologists identify and superselectively catheterize tumor feeders and monitor the completeness of the procedure.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter